This blog post provides step-by-step guidance on how to repair a worn shaft using an injection technique with the high-performance coating, Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal).
This method of a shaft repair is suitable for situations including, but not limited to:
- Restricted access to the shaft
- Confined workspace
- Pre-installed former
- Limited personnel carrying out the repair
Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) exhibits high compressive strength which is crucial for the functionality of the equipment. The application and installation by injection is easy and does not require hot work. The ceramic fillers in this epoxy coating make it exceptional for erosion and corrosion protection, and thus for the longevity of the rotating equipment.
Step-By-Step Guide: Shaft Repair Using an Injection Technique
Step One: Apply Release Agent
Apply Belzona 9411 (Release Agent) to the internal surface of the former.

Step Two: Tape off Repair Area
The repair area is taped off to protect during the application of the release agent to the adjacent areas.

Step Three: Apply Release Agent and Remove Tape
Apply Belzona 9411 (Release Agent) to the area around the shaft repair area and remove the tape.

Step Four: Secure Former
Position the former around the shaft and secure it with fasteners.

Step Five: Mix Epoxy Coating
Thoroughly mix the Base and Solidifier of the two-part epoxy coating, Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal).

Step Six: Fill the Cartridge
Pour the mixed Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) into the cartridge.

Step Seven: Install Nozzle
Cut off the tip and install the nozzle.

Step Eight: Inject the Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal)
Inject the product through the injection port on the bottom of the former.

Step Nine: Remove Excess Product
Remove excess product exuded from the vent port.

Step Ten: Insert Corks
Insert corks into the injection and vent ports.

Step Eleven: Remove Former
Gently remove the former.

Step Twelve: Smooth Out Repair Area
Smooth out the repair area with an emery cloth to remove all sharp edges.

Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a worn shaft?
Before looking at the repair method, it’s important to understand the causes of shaft wear. Factors such as misalignment, corrosion, abrasion, and poor lubrication contribute to shaft wear. Left untreated, this leads to equipment inefficiency and the need for repair.
Instead of expensive shaft replacement, modern industries are turning to polymeric shaft repair techniques that allow for restoring shafts in-situ. This approach avoids hot work, making it a safe shaft repair method in sensitive environments.
What kind of former can you use for shaft repair using the injection method?
Traditionally, stainless steel formers have been widely utilized for shaft repairs. With 3D technology becoming a game changer in the manufacturing world, it is simplifying how repairs can be done. Why 3D technology? Shorter lead time, design flexibility, and lower costs. For this demonstration, we used a 3D former printed so we could compare its performance to that of a stainless steel former. As a result, it performed as expected and helped carry out the application smoothly.
This is not our first attempt at bringing in 3D printing technology to assist with Belzona repairs. In one of our previous blog posts, How to Repair a Live Leak with Belzona 3D Mesh, we demonstrated how to stop a live leak utilizing a 3D printed mesh.
Can injection-based shaft repair be a viable alternative to welding?
Yes — using two-part epoxy systems such as Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) offers a cold, non-heat method for restoring shafts. This alternative to welding avoids thermal distortion, metallurgical changes, and hot-work hazards.
How soon after injection can the shaft be returned to service?
Allow Belzona 1321 (Ceramic S-Metal) to solidify as below subjecting it to the conditions indicated.
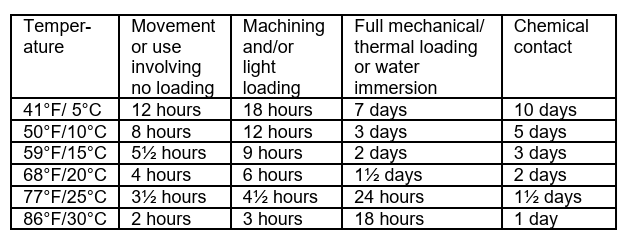
Does this method require complete disassembly of the equipment?
One of the advantages of shaft repair epoxy injection is minimal disassembly. The method is often applied in situ, reducing the need to remove large components — a major advantage in rotating equipment maintenance regimes.
Learn More
Shaft Repair With a Forming Technique: A Complete Guide
How to Rebuild an Oversized Keyway
How to Repair Metal Loss on Pipework (With GIFs and Video)
Video: How to Repair a Worn Shaft Using Injection
Contact Your Local Distributor to Learn More About How to Repair a Worn Shaft
Yulia Burova, Marketing Director, Belzona Inc., Miami FL, USA




What is the minimum allowed clearance between the diameter of former and diameter of the shaft for injection?
Hello Zoran, thank you for you message. At the extent of the repair area, mechanical grinders fitted with suitable cutting discs should be used to undercut the shaft by 1/16 inch (1.5 mm) around the circumference. For more information, please contact your local Belzona representative at: https://www.belzona.com/en/about/disfinder.aspx
Best regards, Belzona Marketing Team