Data centers are mission critical facilities that run operations with profound significance. They are prevalent in industries including healthcare, telecommunications and information technology, BFSI, government and public sector, energy, and many more.(1) Businesses and infrastructures rely on these data centers to store sensitive data and support mission critical applications.
The continuous operation of these facilities in these industries is critical and unplanned downtimes are costly. Therefore, there is a need to protect these data centers. Polymeric technology can offer solutions to these facilities and allow them to continue their critical operation across various industries.
TYPES OF DATA CENTERS
Data centers represent an expansive and profitable market. There are currently three main types of data centers: on-premises, colocation, and cloud.
On-premises. Client company is responsible for their own equipment (owning, using, and maintaining), infrastructure, and entire operating costs (power cost, cooling, communications, data center floor space). Regulations (concerning sensitive data), security, and accessibility are some of the reasons companies choose on-premises data centers. These data centers are becoming less common.
Colocation. Client company is responsible for their own equipment but share operating costs with other companies.2 Some colocation providers also offer maintenance. Regulations, security, shortage of existing data center, secondary back up data center are some of the reasons companies choose colocation data centers.
Cloud: Cloud providers supply the client company with equipment (servers, storage, and network) and manage maintenance in a shared facility with other companies.2 Outsourcing infrastructure management, reduced capital expenditure, operating expenditure, and flexible scalability are some of the reasons companies choose cloud data centers. There is a shift towards these data centers.
Types of collocation data centers
Colocation data centers can be further categorized as carrier-neutral or non-carrier-neutral data centers:
Carrier-neutral: Data center is not bound to any one service provider (telecommunications, ISP, etc.). This is popular as it provides customers with more options (price, bandwidth, etc.). They tend to be in areas with high competition.
Non-carrier-neutral: Data center is bound to one service provider.
Downtime in Data Centers
The cost of downtime for data centers has been thoroughly researched by Ponemon Institute, sponsored by Emerson Network Power, since 2010. A research paper is published every 3 years with the latest one published for 2016. The study for 2016 analyzed 63 data centers ranging in industries from communications to healthcare to transportation. Out of the 63 data centers, 10 were colocation data centers. The average square footage of the data centers analyzed were 14,090 sq. ft. with a maximum square footage of 55,000 sq. ft. (8) The colocation data centers are most likely on the higher end in terms of square footage.
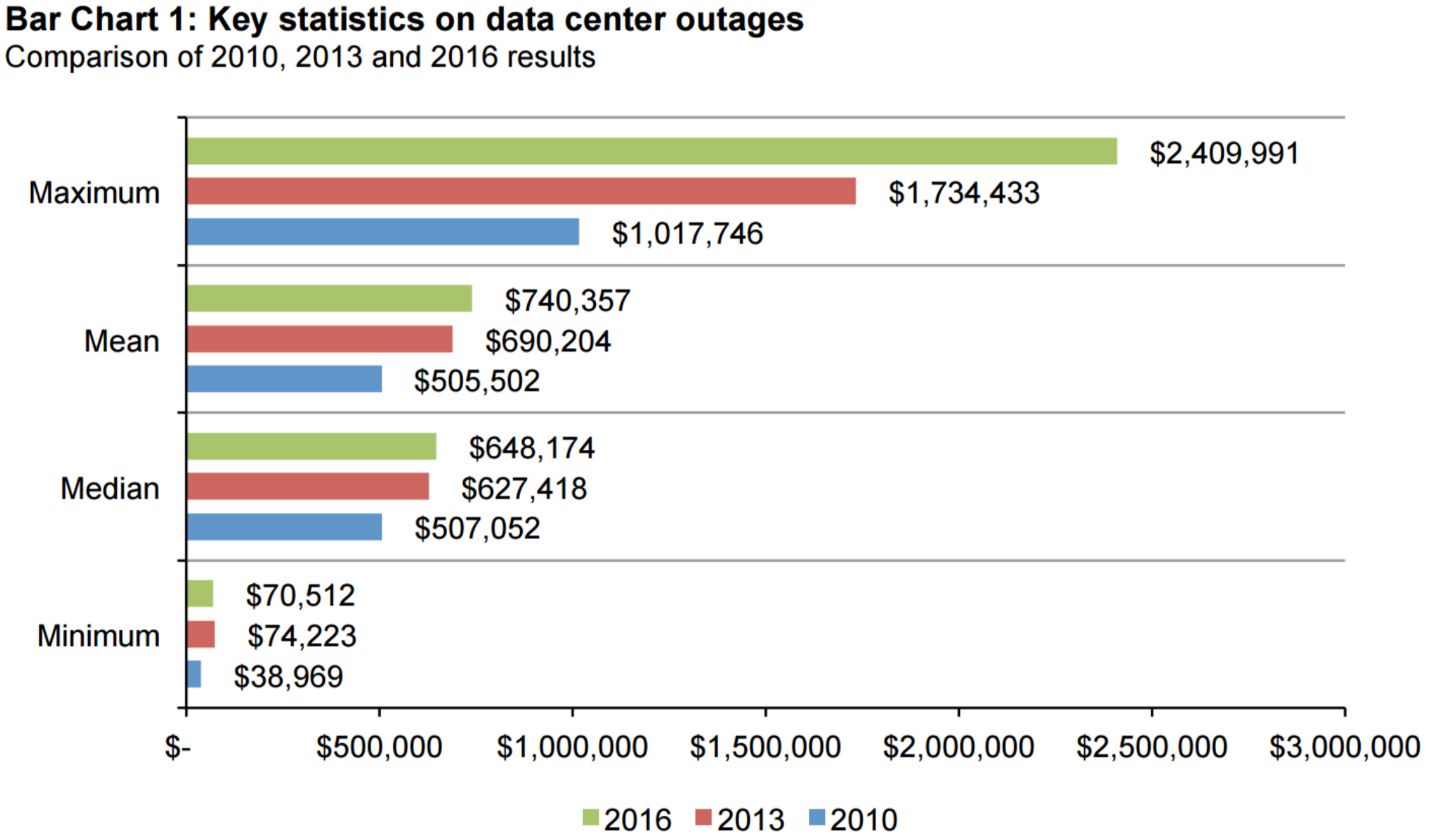
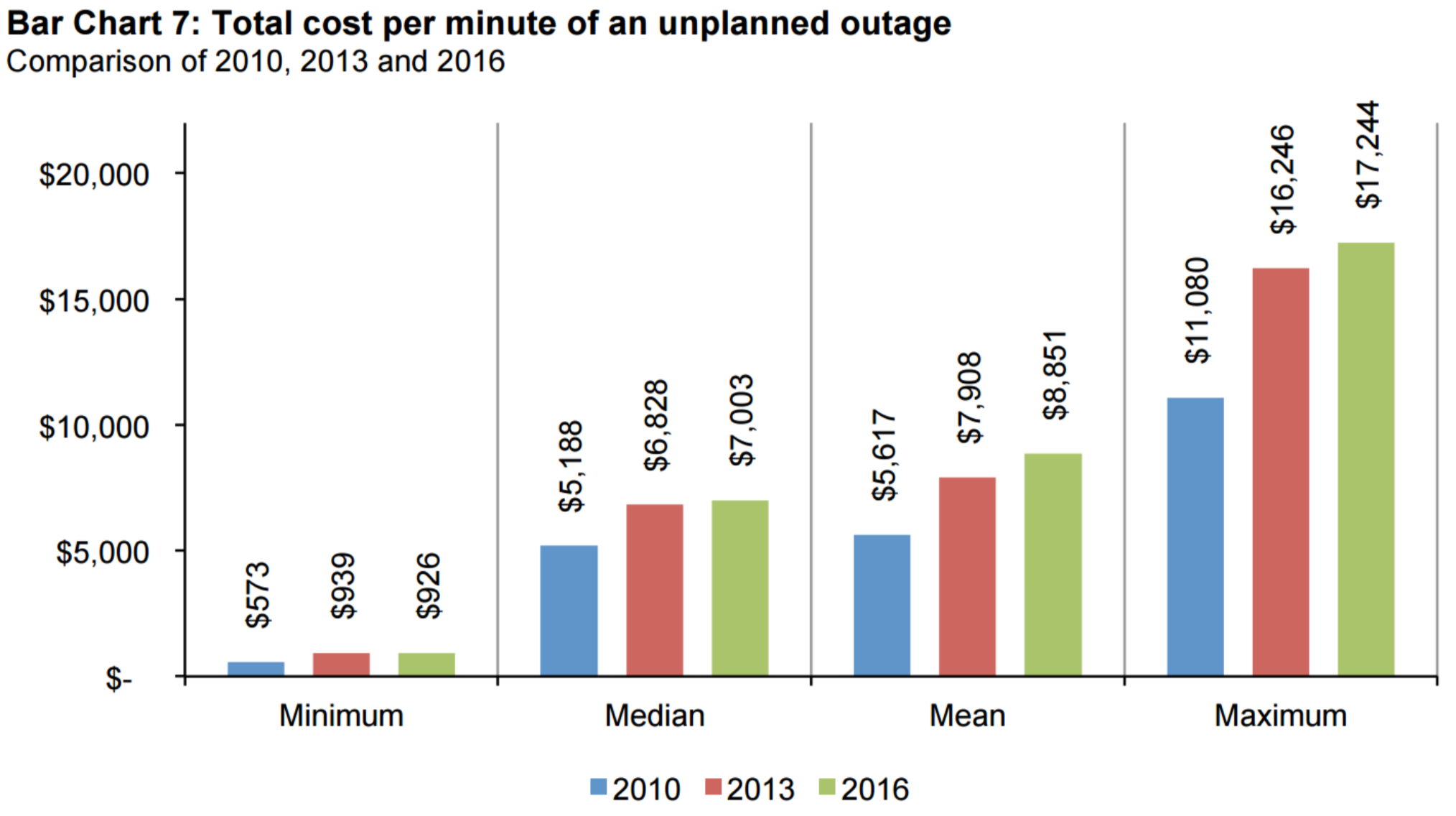
According to the study for 2016, the average cost per minute and average total cost of an unplanned outage was around $9,000/minute and $740,000, respectively. The total cost of an unplanned outage was as high as $2,400,000. Colocation data centers are most likely on the higher end of the costs due to the larger sizes. The majority of costs come from lost revenues and business disruptions. It is important to note that the cost of outages has steadily increased since 2010. (8) This trend may only continue as businesses become more and more dependent on data centers.
Preventative vs. Reactive Maintenance
The importance of preventative maintenance in data centers cannot be overstated. The contrary to preventive maintenance is reactive maintenance. Under reactive maintenance, repairs are only carried out after the equipment has broken down. About 55% of the maintenance in the average facility is conducted under reactive maintenance and the percentage is notably higher in data centers.
Maintenance in data centers includes HVAC system, Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), generators and building. The cost of maintenance in data centers is roughly 2% of the annual budgets. However, there are many unintended consequences of reactive maintenance that is often overlooked. Repairing equipment after it is broken means that there can be loss or corruption of data, shorter life time expectancy of equipment, increased energy costs, inefficient use of resources, and safety issues. This all leads to higher costs in the long-term. There is also the added complication of being unable to control maintenance budgets.
By implementing preventative maintenance, data centers can reduce emergency repairs and unplanned downtime. Problems can be fixed before they become serious. In addition, preventative maintenance leads to system reliability. (10)
Temperature and humidity
It is important to monitor the temperature and humidity in data centers. Electronics generate heat during operation that needs to be dissipated. If the heat is not dissipated and the temperature is too high, electronics can experience reduced efficiency and even failure. In data centers, the high number of electronics operating leads to a high heat generation that needs to be constantly cooled. Normally, higher end equipment automatically shut down when the temperature is too high. A shutdown results in downtime. In addition, the system will usually experience computation errors and application errors before it shuts down.
The cooling fans in the system may be overworked during this time as well, reducing life time expectancy of the equipment. With equipment that does not have this automatic shutdown, the consequences of high temperatures are more severe. Low humidity can cause buildup of static electricity on the equipment and high humidity can cause corrosion to occur on the equipment. In order to prevent any reduced efficiency and downtime in these data centers, it is crucial to control the temperature and humidity.
There are three key areas to measure temperature at a data center: the bottom front of the rack (where the coldest cold air should be), the top front of the rack (where the hottest cold air should be), and the top back of the rack (where the hottest hot air should be). These three areas can be checked to ensure the temperature is not too high. The recommended cold air (front of the rack) temperature should be 64-80°F. The recommended hot air (back of the rack) temperature should have less than 35°F difference from cold air, typically less than 105°F. The humidity should be 40-60% relative humidity. (11)
Types of HVAC systems in data centers
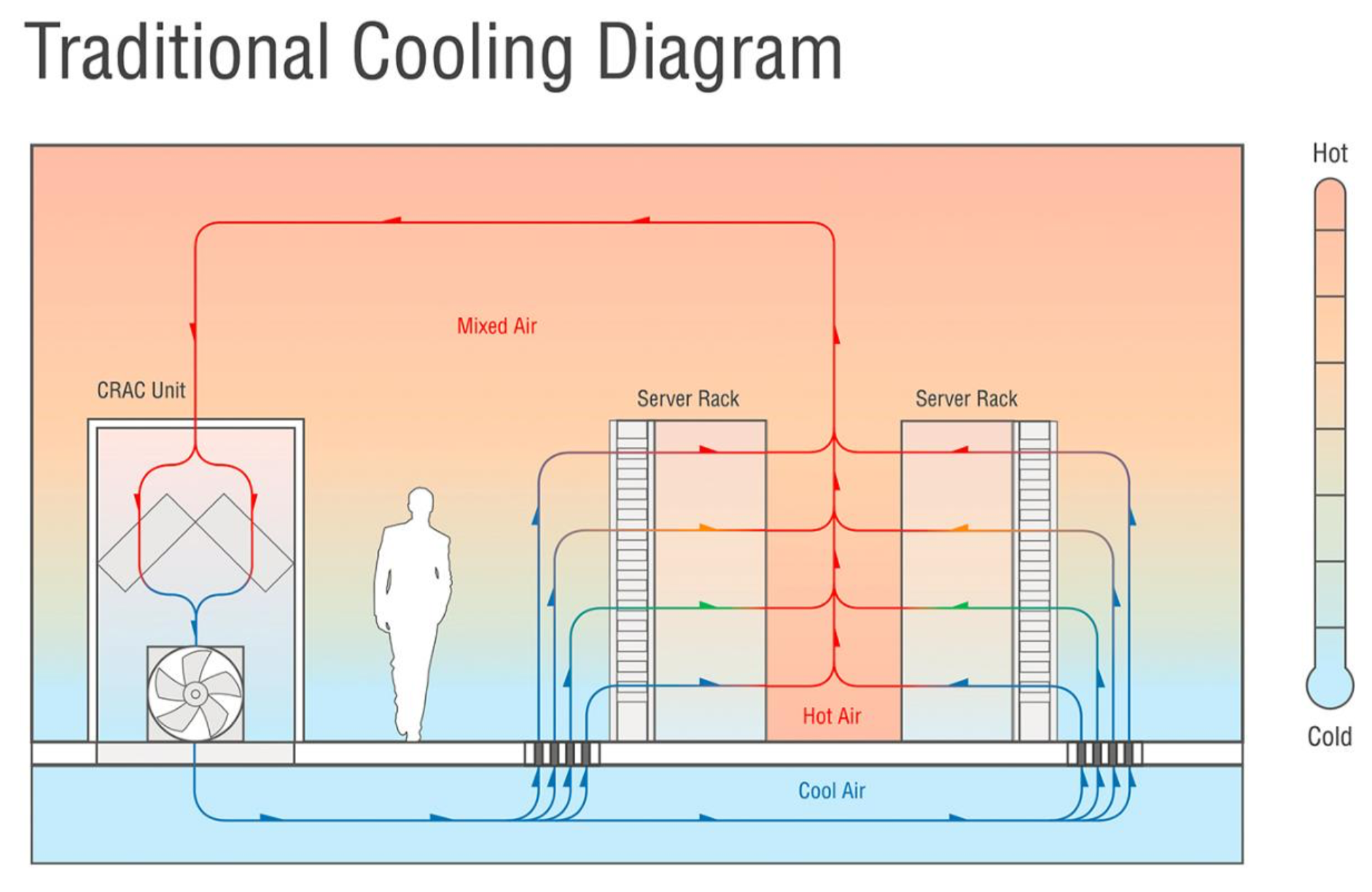
Due to the importance of temperature and humidity control, data centers place emphasis on HVAC systems. There are two main types of HVAC systems for data centers: CRAC and CRAH.
CRAC (Computer Room Air Conditioner): Air is cooled by a cooling coil with refrigerant.12 Similar idea to HVAC systems in small buildings. Generally used in smaller data centers.
CRAH (Computer Room Air Handler): Air is cooled by a cooling coil with chilled water and the chilled water is cooled through the combination of chiller and cooling tower.12 Similar idea to HVAC systems in large multi-story buildings. Generally used in larger data centers.
Types of HEX failure
Heat exchangers can experience failure for many reasons. There are four main types of heat exchanger failure: mechanically, chemically induced corrosion, mechanically and chemically induced corrosion, and fouling. (13)
MECHANICALLY
– Water Hammer: Interruption in the flow of cooling water can cause pressure surges or shock waves that damage metal
– Vibration Fatigue: Excessive vibration from equipment or fluid flow can cause fatigue stress crack and erosion at welded joints
– Thermal Fatigue: Thermal cycling can accumulate stresses and cause cracks
– Freeze-Up: Temperature drops below the freezing point of cooling water in water cooled heat exchanger
CHEMICALLY INDUCED CORROSION
– General Corrosion: Slow, uniform corrosion of the metal
– Pitting: Localized corrosion of the metal
– Stress Corrosion: Attacks on the metal grain boundaries in stressed areas causing cracks
– Dezincification: Zinc is chemically removed from copper-zinc alloys leaving a porous surface
– Graphitization: Graphite is formed in iron or low-alloy steels leaving a weak material
– Galvanic Corrosion: Corrosion occurring from dissimilar metals
– Crevice Corrosion: Corrosion occurring in secluded areas
MECHANICALLY AND CHEMICALLY INDUCED CORROSION
– Erosion-corrosion: Corrosion effects are accelerated as protective films and corrosion products are removed from erosion, leaving deeper layer of metal surface exposed to corrosion
– Corrosion-fatigue: Similar idea to erosion-corrosion. Corrosion effects are accelerated as protective films and corrosion products are removed from cyclic stresses, leaving deeper layer of metal surface exposed to corrosion
FOULING
– Scale: Dissolved mineral precipitating out of cooling water
– Suspended solids: Sand, iron, silt, and other visible particles in cooling water that can cause abrasion
– Algae (other marine growth): Environment in heat exchanger promotes algae and other marine growth
The exposure of cooling towers to the environment are usually the cause of fouling. The fans in cooling towers are used to evaporate the cooling water using ambient air. The pollutants in the ambient air used in this process can contaminate the cooling water. Animal and vegetable matters can contaminate the cooling water as well since the cooling towers are exposed to the environment. (13)
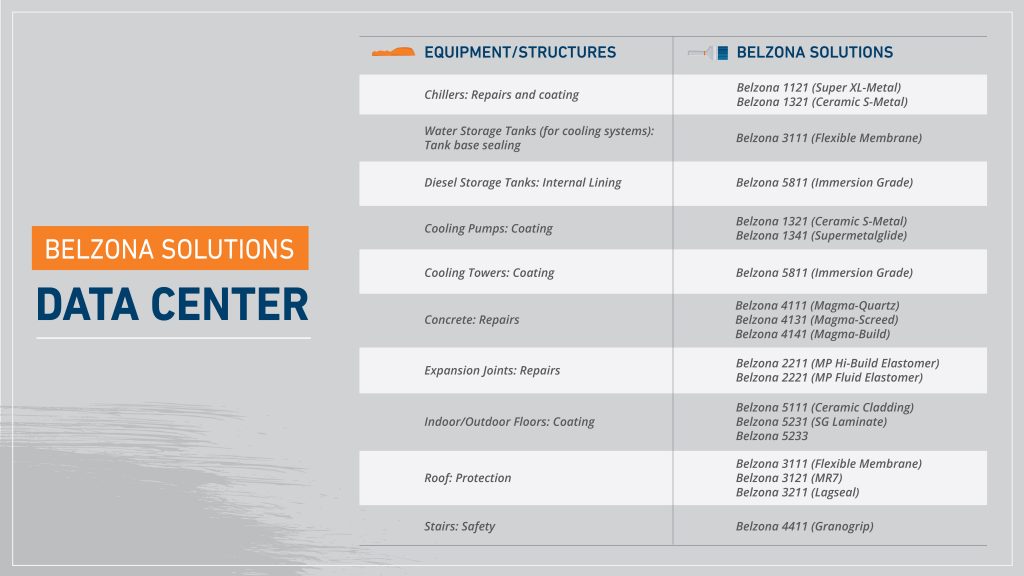
Belzona already has many of the solutions that data centers require for HVAC maintenance: chiller tube sheets repair and protection, HEX leak sealing, air handler condensate and drain pan sealing and lining, sealing of joints and seams in cooling tower pans.
Data centers also frequently require concrete and expansion joint repairs, step repairs, non-skid floor coatings, safety grips systems, sidewalk, entry concrete repairs, fountain leak sealing and protective lining, floor coatings, uneven threshold transition repairs. The pipes that carry chilled water may need repair and erosion-corrosion protection to prevent leakage and stairs may need grip systems for safety.
WANT MORE INFORMATION ABOUT DATA CENTERS MAINTENANCE SOLUTIONS?
REFERENCES
- http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/colocation-market-1252.html (Data Center Industries)
- http://www.forbes.com/sites/sungardas/2013/10/29/how-to-choose-between-cloud-and-colocation-services/#3d64c5e93d1b (Colocation vs Cloud)
- http://www.telx.com/blog/why-is-carrier-neutrality-so-important/ (Carrier-Neutral vs Non-Carrier-Neutral)
- http://energy.gov/eere/articles/10-facts-know-about-data-centers (Overall Data Center Numbers)
- http://www.datacentermap.com/ (Colocation Data Center Numbers)
- http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/us-data-center-construction-market-2015—2019-green-data-centers-are-the-latest-trend-observed-497238831.html (Data Center Construction Growth)
- http://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/27/realestate/commercial/texas-lures-data-centers-not-for-jobs-but-for-revenue.html (Multi-tenant Data Center Revenue)
- http://www.emersonnetworkpower.com/en-US/Resources/Market/Data-Center/Latest-Thinking/Ponemon/Documents/2016-Cost-of-Data-Center-Outages-FINAL-2.pdf (Ponemon InstituteStudy)
- http://www.datacenterknowledge.com/special-report-the-worlds-largest-data-centers/largest-data-centers-worthy-contenders/ (Data Center Sizes)
- http://www.datacenterjournal.com/datacenter-facilities-maintenance-time-change-culture/ (Reactive vsPreventive Maintenance)
- https://serverscheck.com/sensors/temperature_best_practices.asp (Data Center Temperature and Humidity)
- http://www.mcrinc.com/Documents/Newsletters/201305_DifferentWaysToCoolDataCenters.pdf (Center Cooling)
- https://www.mts.com/ucm/groups/public/documents/library/mts_004900.pdf (Heat Exchange Causes)
Charts and Graphs
A. http://www.emersonnetworkpower.com/en-US/Resources/Market/Data-Center/Latest-Thinking/Ponemon/Documents/2016-Cost-of-Data-Center-Outages-FINAL-2.pdf
B. https://journal.uptimeinstitute.com/a-look-at-data-center-cooling-technologies/
Yulia Burova, Marketing Director, Belzona Inc., Miami FL, USA



